“A Paradigm Shift from Thermal to Renewables”
Introduction
India is witnessing a remarkable transformation in its energy landscape, driven by the urgent need to transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy (RE) sources. With increasing global focus on sustainability and a surge in energy demands due to factors like data centers, electric vehicles (EVs), and industrial expansion, India’s push for green energy is gaining momentum. This blog explores the evolution of renewable energy in India, the decline of thermal energy, government initiatives, and global developments influencing India’s RE sector.
What is Green Energy?
Green energy refers to energy generated from natural, renewable sources that have minimal or no negative impact on the environment. The primary characteristic of green energy is its sustainability and its ability to produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions during generation.
An Increase in use of Renewable energy generally contributes to an increase in production of green energy, causing less damage to the environment while meeting the energy requirements of India
Increasing Trend in Installed Capacity
India has made significant strides in expanding its renewable energy capacity.
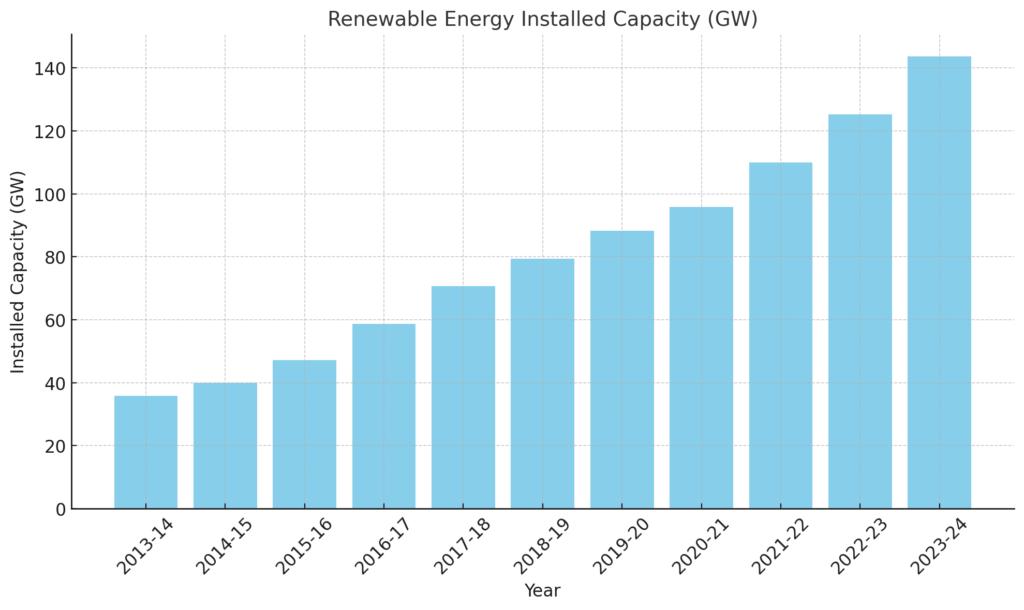
We witness a steady growth from 35.8 GW in 2013-14 to 143.6 GW in 2023-24 of the Installed Capacity of Renewable Energies in India.
This indicates a positive trend towards increasing India’s potential to actually generate energy from clean sources to cope up with increasing per-capita consumption (energy demands) and declining deficit (capitalizing the increasing energy demands) as discussed in Power Sector of India blog.
As discussed in Participants in the Indian Power Sector blog, 53.2% of India’s energy produced is from Fossil fuel, which have high carbon emission, with the world advancing ahead, concerns regarding sustainability arise. ,
Hence India’s energy generation sources must change to Green energy sources to benefit towards India’s growth.
Change in Trend: Shift from Thermal to Renewable Energy
Though more than 50% of India’s Energy is derived from thermal sources, the trend seems to be changing, various government initiatives and targets indicate a more favor towards the Renewable energy.
Producing energy from Renewable sources ensures India with energy security as by diversifying the energy mix with renewables, India can reduce dependence on imported fuels.
This shift not only mitigates the risks associated with volatile global oil and coal prices but also promotes environmental sustainability.
India’s capacity addition trends reveal a decisive shift from thermal energy to renewables. Below are the annual capacity additions for both thermal and renewable sources:
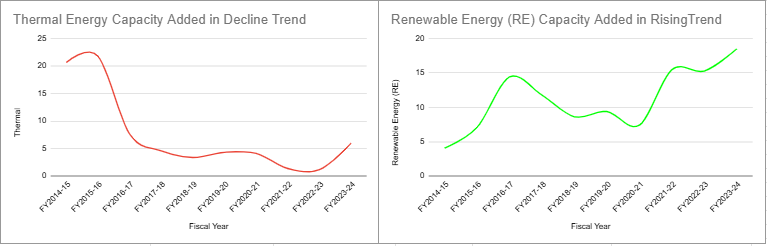
- Thermal Energy: Displays a steady decline in addition of capacity from 20.64 GW added in FY2014-15 to 5.95 GW added in FY2023-24.
- Renewable Energy: Shows a rising trend, reaching 18.49 GW in FY2023-24.
From the above data, it becomes evident that the capacity added to produce energy from thermal sources is reducing, more investments are being allocated to the installed capacity of Renewable Energies.
The reliance on imported coal exposes India’s power generation sector to global market fluctuations, affecting fuel costs and energy pricing. To mitigate these challenges, India is focusing on increasing domestic coal production and accelerating the adoption of renewable energy sources. This strategy aims to enhance energy security, stabilize electricity costs, and reduce environmental impacts associated with fossil fuels.
India’s Renewable Energy Targets
India has set ambitious renewable energy goals to transition toward a greener future:
- Achieve 500 GW of non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030.
- Reduce carbon intensity by 45% by 2030 compared to 2005 levels.
- Attain net-zero carbon emissions by 2070.
Why Renewable Energy?
We have already discussed the reasons as to why there is an opportunity in the Power sector of India, but why would a company generating energy would move from a fossil based (already available infra) energy to renewable based energy.
- Electricity Demand Surge: Emerging sectors such as data centers, EVs, and electric steel are driving electricity demand. For instance:
- Data centers’ power consumption is expected to double from 460 TWh in FY2022 to 1,000 TWh by FY2026.
- EV adoption increases household electricity demand by 20-50%, according to Boston Consulting Group.
- Shorter Construction Timelines: With upcoming rising surge in energy demand, India require more power generating plants, a 500 MW solar plant can be constructed within 18 months, whereas thermal or hydro plants may take 2-3 times longer.
- Cost of Electricity Production: Rising coal prices increase the operational costs for coal-fired power plants, leading to higher electricity prices for consumers.
- Investment Decisions: Persistent high fossil fuel prices can make renewable energy projects more economically attractive, influencing long-term investment strategies toward sustainable energy sources.
- Fuel Switching: Elevated natural gas prices can prompt a shift back to coal for electricity generation in key markets, including the United States, Europe, and Asia, as observed in recent years. This switch can lead to increased CO₂ emissions from electricity generation globally and increase the prices of coal as the demand for coal increases.
Policies and Initiatives by the Government of India
Of course to promote such change and meet the Renewable energy target, the India’s government has introduced several incentives to promote renewable energy:
Tax Benefits:
- Section 80-IA: 100% tax exemption on profits for 10 years for solar, wind, biomass, and hydro projects.
- Accelerated depreciation (40%) for solar, wind, biomass, and small hydro projects.
GST Benefits:
- 5% GST on solar and wind equipment, compared to 18-28% for thermal equipment.
Other Incentives:
- Waiver of Inter-State Transmission System (ISTS) charges for solar and wind projects commissioned before June 30, 2025, for 25 years.
- Net metering policies enabling system owners to sell excess electricity back to the grid.
- Capital subsidies (up to 30%) for residential rooftop solar installations.
Global Developments and Their Impact on India
India is not isolated from the world, each development across the globe impacts India.
Let us spot some global developments across the world that could later on be considered in India as an investment option:
- China: Planned increase in grid capital expenditure from $102 billion (2023) to $157 billion by 2030 highlights the global pivot to renewables. India can attract foreign investments by improving its grid infrastructure.
- Europe: Growing investments in hydrogen-based projects can inspire India to develop similar technologies.
Advantages for Renewable Companies Over Fossil-Based Companies
India keeps promoting Renewable through a bunch of schemes and initiatives, so when investing in the companies involved in this sector, it becomes useful to compare the fundamental advantages that the company receives that would later on reflect on the financials.
| Benefits | Renewable Energy Companies | Fossil-Based Companies |
| Tax Holiday | 10 years under Section 80-IA | Limited to new projects |
| Accelerated Depreciation | 40% | Standard (15%) |
| GST Benefits | 5% | 18-28% |
| Subsidies | Capital, state-level incentives | Minimal |
| Transmission Charges Waiver | Yes | No |
Companies involved in Renewable Energy
| Company Name | Business Type | Major Source | P/E Multiple | Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suzlon Energy | Pure-play | Wind | 72 | 7.5 (Good) |
| NTPC Green Energy | Pure-play | Solar | 200 | 6.0 (Weak) |
| Adani Green Energy | Conglomerate | Solar | 103.47 | 6.8 (Average) |
| KPI Green Energy | Conglomerate | Solar & Wind | 29.88 | 6.7 (Average) |
Conclusion
India’s renewable energy revolution is a testament to its commitment to sustainability and energy security, integrating renewable energy into the power generation mix not only strengthens energy security by reducing dependence on imported fuels but also insulates the economy from the volatility of global oil and coal markets. This transition supports sustainable economic growth and environmental stewardship. With robust government support, global investments, and growing energy demands from new-age sectors, the future of renewables in India looks promising. However, sustained focus on infrastructure, policy execution, and innovation will be critical to achieving its green energy ambitions.
India is not just transitioning to renewable energy—it is leading a revolution that has the potential to inspire the world.
Disclaimer
This report has been prepared solely for informational purposes based on publicly available data and sources deemed reliable. The author has exercised reasonable care to ensure the accuracy of the data used; however, neither the author nor their organization guarantees the completeness or accuracy of this report and disclaims all liability for any loss or damage arising from its use. The author affirms that this report has been prepared independently, without any conflict of interest or financial compensation from any company or entity mentioned herein.
Data sources:
Central Electricity Authority.
Ministry of Power.
Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MOSPI).
The Press Information Bureau (PIB).
IBEF’s reports.
Finkhoz Platform
Company-specific information: sourced from annual presentations and official websites.



